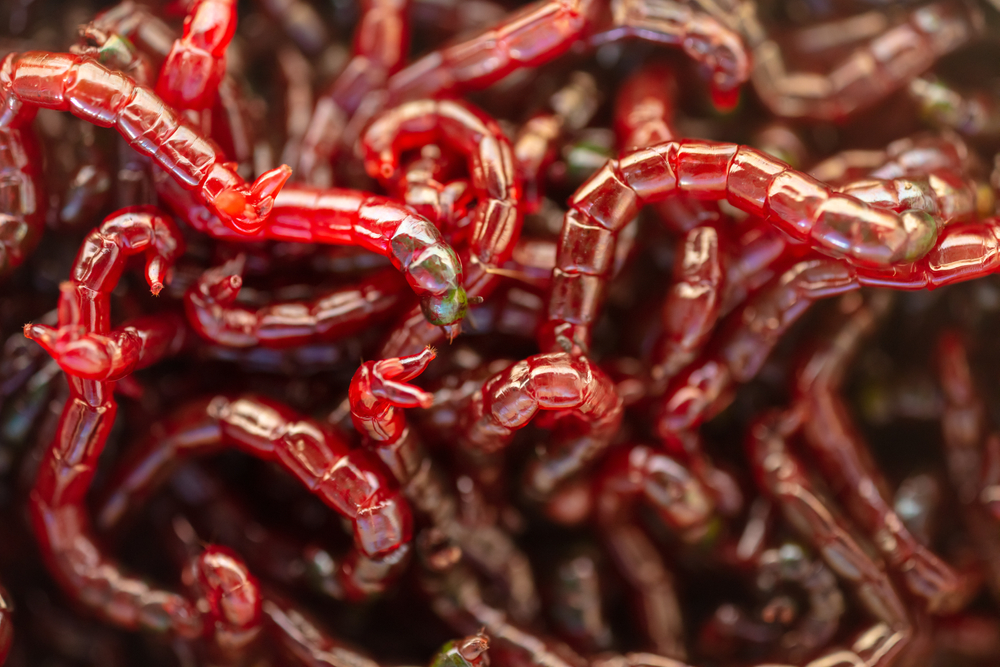
Bloodworms are recognized as a staple in the diet of betta fish, favored for their nutritional value and palatability. These larvae of non-biting midges are typically available in live, frozen, or freeze-dried forms, each with its own benefits and drawbacks.
Betta fish, with their carnivorous nature, often show great enthusiasm when presented with bloodworms, which can serve as a high-protein snack.
Betta owners should, however, be aware of the risks associated with overfeeding and the potential for nutritional imbalances or health issues that can arise from improper dietary practices.
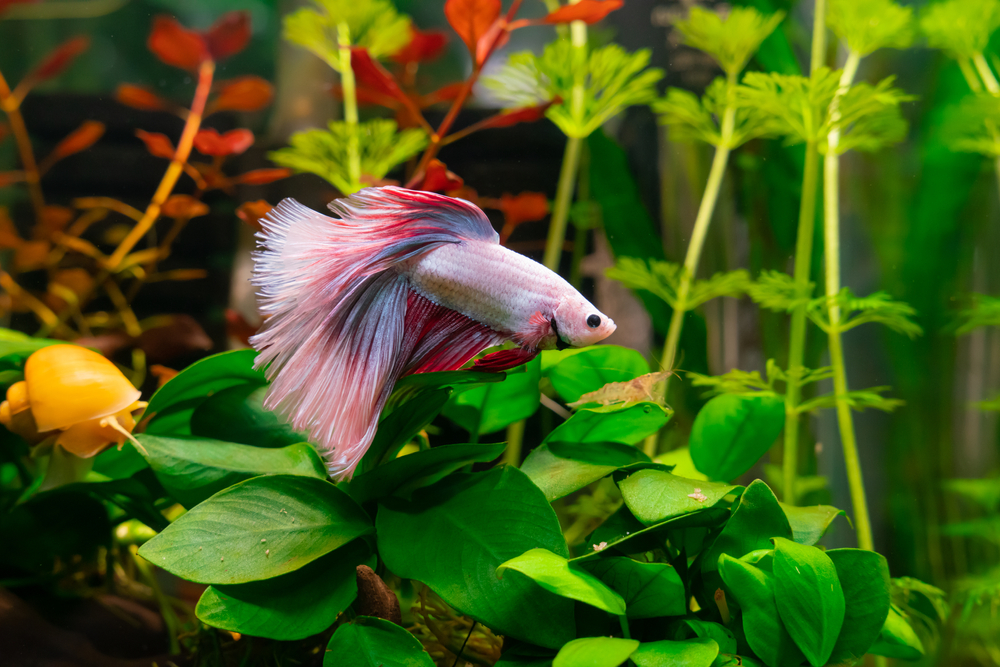

Understanding the nutritional profile of bloodworms is essential for integrating them into a betta fish’s diet effectively. Although these worms provide an excellent source of protein, they should be offered as a supplement to a more varied diet that provides all the necessary nutrients betta fish require.
Additionally, identifying high-quality bloodworms and adhering to safe feeding practices are imperative to avoid introducing diseases and ensuring the overall well-being of these aquatic pets.
Contents
Key Takeaways on Blood Worms for Betta
- Bloodworms are a popular, protein-rich food choice for betta fish but should not be the sole dietary component.
- Overfeeding bloodworms can lead to health issues, thus requiring moderation and dietary variety for bettas.
- Quality and safe handling of bloodworms are crucial to prevent disease and maintain betta fish health.
You will also like these other posts:
Understanding Bloodworms
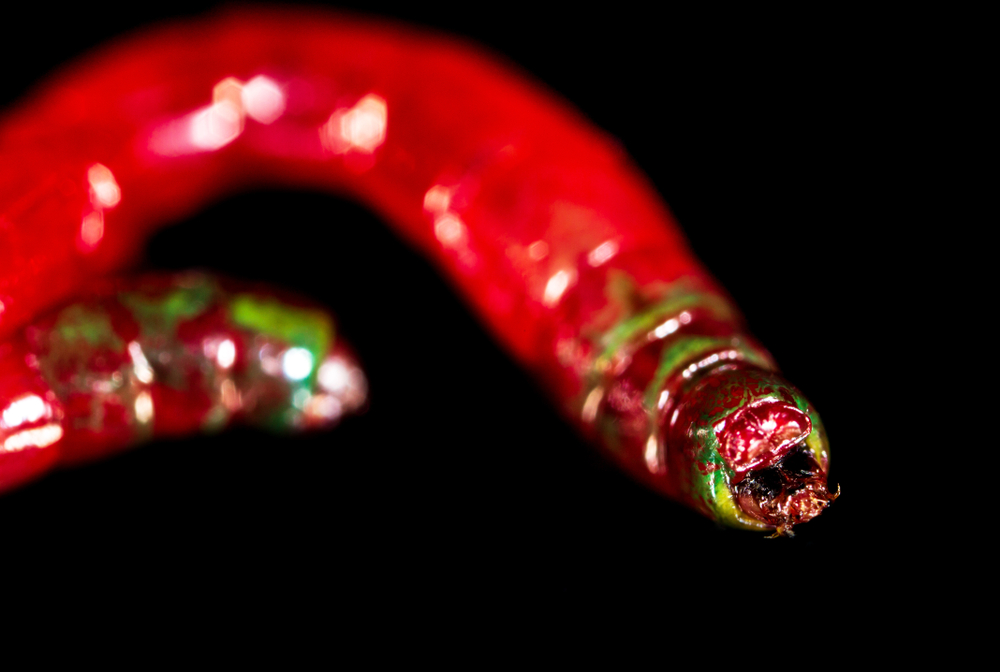

Bloodworms serve as a popular dietary choice for betta fish, praised for their protein content, but caution is needed in terms of their nutritional completeness and potential overuse.
Types of Bloodworms
Bloodworms can come in three different forms: live, frozen, and freeze-dried. Each type offers different benefits and drawbacks when it comes to feeding betta fish.
- Live Bloodworms: These are the larvae of midge flies in their natural, live state. Offering the most natural feeding experience for betta fish, live bloodworms can stimulate a betta’s hunting instincts. Also, since they are in the larval stage, they move in the water, providing an enticing meal for fish. However, live bloodworms pose the risk of carrying diseases that can be transmitted to the aquarium inhabitants.
- Frozen Bloodworms: These are live bloodworms that have been frozen to kill parasites and pathogens, making them safer to feed than live bloodworms. Frozen bloodworms retain most of the nutritional value of live ones and are convenient to store.
- Freeze-Dried Bloodworms: Freeze-dried options offer the longest shelf-life and eliminate the risk of introducing pathogens to the tank. Nevertheless, the freeze-drying process can strip away some of the nutrients found in live bloodworms, and they don’t offer the same stimulation for bettas as live or frozen types do.
Bloodworms are derived from the larvae of midge flies or, less commonly, from the marine worm Glycera, which are segmented worms more often used for marine fish. As a larval stage food source, they are naturally part of many freshwater fishes’ diets, including bettas.
However, bloodworms should not be the only food source for bettas as they lack the vitamins and minerals found in a more varied diet.
The Nutritional Profile of Bloodworms
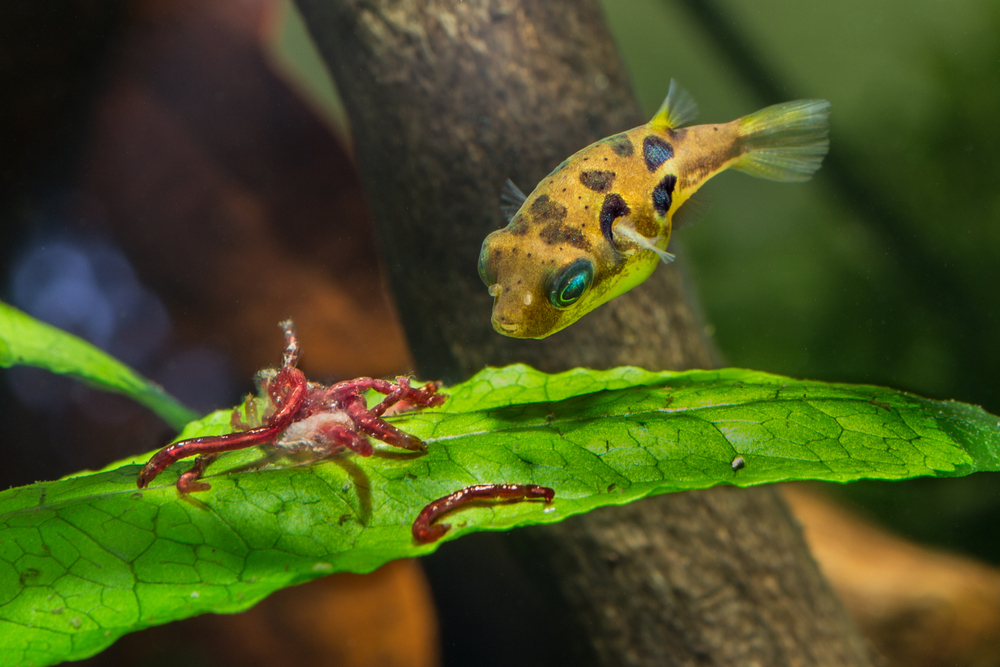

Bloodworms offer a high protein and fat content beneficial for betta fish, yet it’s important to consider the balance of nutrients and potential risks.
Nutritional Benefits for Betta Fish
Bloodworms are a protein-rich food source, providing essential amino acids that support the growth and maintenance of betta fish. They also contain a modest amount of fat, which is crucial for energy.
While live or frozen, bloodworms can also offer vitamins, including vitamin B12, and minerals such as iron, which are important for a betta’s health. The inclusion of natural carotenoids in bloodworms can enhance the betta’s vibrant coloration.
Risks and Considerations
Nonetheless, bloodworms lack some nutritional value that betta fish require, and should not be the only food source. Overfeeding can lead to obesity due to high fat content.
Additionally, there’s a risk of bacteria, parasites, and contaminants with live bloodworms that could harm betta fish. It is crucial to source bloodworms from reliable suppliers to minimize these risks. However, frozen or freeze-dried bloodworms typically have a lower risk of transmitting diseases compared to live ones.
How Bloodworms Fit into a Betta’s Diet
Bloodworms offer high protein content for betta fish, which can be a tantalizing treat, but they must be integrated carefully to maintain a balanced diet.
Balancing the Diet with Variety
A balanced diet for a betta includes a variety of nutrients that bloodworms alone cannot provide. Betta fish thrive when their diet is a mix of pellets, flakes, and live or frozen foods like bloodworms and brine shrimp.
It’s important to ensure that bloodworms complement these staples without overshadowing them to meet all of a betta’s dietary needs.
Frequency and Quantity of Bloodworm Feeding
When feeding bettas bloodworms, moderation is key. They should be given as part of the weekly feeding regimen, but not more than once or twice a week in small quantities.
An optimal serving size would be just enough that the betta can consume within a few minutes, preventing overfeeding and potential health issues.
Special Dietary Considerations
While bloodworms are high in protein, they lack some essential vitamins and minerals that bettas require. It is crucial to use bloodworms as a supplement to a well-rounded diet that provides the full spectrum of nutrients.
All dietary adjustments should take into account the betta’s age, health, and activity level to ensure their overall well-being.
Safe Feeding Practices

Proper feeding with bloodworms ensures that betta fish receive high nutrition without negative health impacts. The key is managing the quantity and condition of the bloodworms’ provision.
Preparation and Storage Methods
It is imperative to store bloodworms correctly to maintain their nutritional integrity. They can be offered to betta fish either live, frozen, or freeze-dried.
Live bloodworms should be kept in a cool environment and used within a short period, while frozen varieties need to be stored at consistent freezing temperatures. Prior to feeding, thawed bloodworms must be rinsed with clean water to prevent potential water contamination.
Avoiding Overfeeding and Health Risks
Overfeeding betta fish with bloodworms can lead to serious health concerns. They should be fed bloodworms often but in moderation, as part of a varied diet to prevent issues like bloating and digestive issues.
Bloodworms are rich in protein, and whereas providing nutritional benefits, excessive consumption can cause swim bladder disease, which affects the fish’s buoyancy. It’s advisable to limit feedings of bloodworms to a couple of times per week to avoid these risks.
Identifying Quality Bloodworms
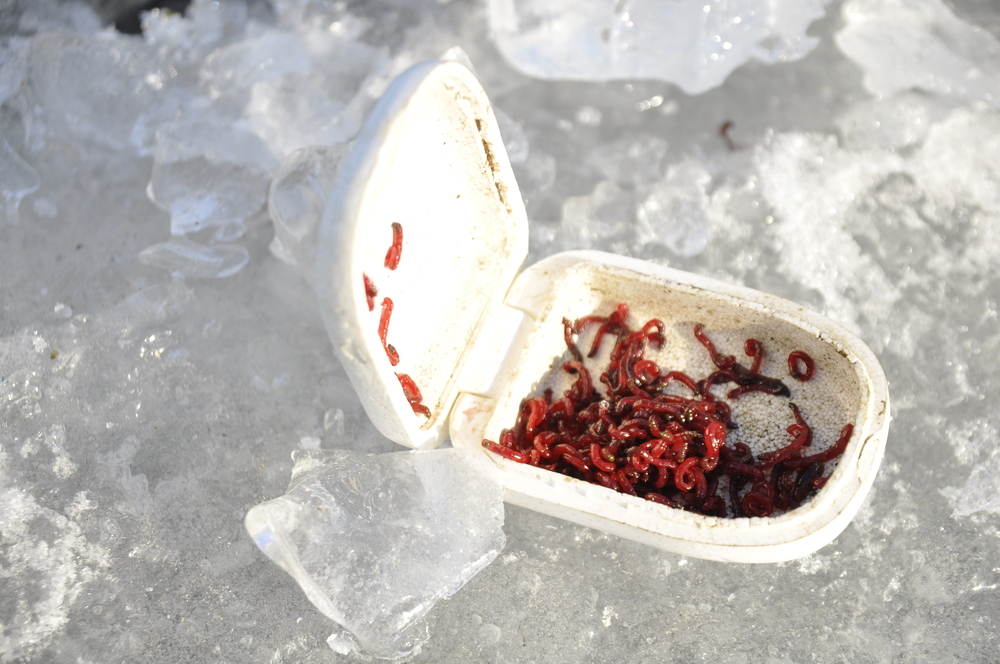

When selecting bloodworms for betta fish, it’s essential to understand the difference between grades and recognize signs of freshness, ensuring the health and happiness of your pet.
Grade A and Grade B Bloodworms
Grade A bloodworms are often considered the premium choice for betta fish. They are typically characterized by their vibrant red color, signifying a rich hemoglobin content and optimal nutrition. In contrast, Grade B bloodworms may appear duller and are often smaller in size, potentially indicating a lower nutritional value.
Freshness and Signs of Quality
Freshness in bloodworms is crucial. High-quality, fresh bloodworms have a firm texture and lack any unpleasant odor. Look for packages that are sealed properly and do not have excess liquid, which can be indicative of decay.
When considering frozen bloodworms, ensure they are free of freezer burn and the blocks are not broken up, which can point to thawing and refreezing.
Potential Problems with Bloodworms
While bloodworms can be a nutritious treat for betta fish, they also present potential risks if not managed properly. This section outlines the specific concerns related to water quality and fish health.
Impact on Water Parameters
1. Ammonia Spikes: Overfeeding bloodworms may lead to uneaten remnants decaying in the tank, which can result in harmful ammonia spikes. Regular monitoring and maintenance of water parameters are essential to prevent this issue.
2. Water Quality: The water parameters can become imbalanced with excessive feeding of bloodworms. This imbalance often manifests in heightened levels of nitrates and ammonia, which necessitates vigilant testing and water changes to maintain a healthy environment.
Health Complications
1. Constipation: Bloodworms, particularly when used as a sole food source, can cause constipation in betta fish. To avoid blockages, they should be fed in moderation as part of a varied diet.
2. Swim Bladder Disorders: Overindulgence in bloodworms may lead to swim bladder disorders due to digestive distress. Ensuring a balanced diet with adequate fiber helps mitigate these health problems.
3. Parasitic Infections: An additional concern with bloodworms is the potential introduction of parasites, which can lead to serious health complications if the bloodworms are not sourced from a reputable provider or if they are not properly prepared before feeding.
Enhancing Betta Health and Enrichment
Providing betta fish with proper nutrition and environmental enrichment is crucial for their overall well-being. Tailored feeding strategies can emulate natural conditions, supporting not just the physical health but also the behavioral vitality of these fish.
Fostering Natural Behavioral Traits
Bloodworms, when introduced to a betta’s diet, can trigger a betta’s hunting mode, which is a critical aspect of their natural behavior.
Feeding live or frozen bloodworms encourages the betta to chase and capture prey, offering significant mental stimulation that mirrors their wild instincts. Such environmental enrichment can reduce stress and promote vibrant health.
Benefits of Varied Feeding Schedules
Implementing a varied feeding schedule can prevent bettas from becoming picky eaters while ensuring they receive a range of nutrients. For instance, supplementing a betta’s diet with bloodworms two to three times a week can bolster their intake of essential proteins.
However, as they are prone to overfeeding, it’s essential to provide them with a balanced diet that caters to their specific needs, including periods of fasting to mimic their natural feeding patterns, which can be beneficial for breeding conditions as well.
Sourcing and Selecting Bloodworms
When looking for bloodworms, aquarium hobbyists should prioritize finding suppliers that offer high-quality, well-preserved stock. Understanding the labeling will also help ensure that the bloodworms are suitable for their carnivorous fish, such as betta.
Finding Reputable Suppliers
Aquarium enthusiasts should purchase bloodworms from reputable suppliers to guarantee the health and vitality of their betta fish. Key indicators of a trustworthy source include:
- Transparency: Suppliers should provide clear information about the origin and handling of their bloodworms.
- Reviews: Positive feedback from other hobbyists can serve as a testament to the supplier’s reliability.
Additionally, those engaged in the aquarium hobby can refer to online forums or local aquarium societies for supplier recommendations.
Understanding Labels and Packaging
Proper labeling and packaging are critical in selecting the right type of bloodworms for betta fish. They can typically be found live, frozen, or freeze-dried. Here’s what aquarists should look out for:
- Ingredients list: For freeze-dried bloodworms, the packaging should list only bloodworms without unnecessary additives.
- Sealed Packaging: Frozen bloodworms should be sealed properly to avoid freezer burn and maintain nutritional integrity.
- Expiration Date: Always check for the freshness of the product, which is especially crucial with live and frozen varieties.
In sum, careful selection from trusted sources, combined with an understanding of product labeling, ensures that aquarists provide healthy, nutritious food for their betta fish.
Frequently Asked Questions
Bloodworms are a popular choice for betta fish owners due to the nutrients they provide. Yet, it’s important to know how to feed them properly to ensure the health and vitality of betta fish.
What are the benefits of feeding bloodworms to betta fish?
Bloodworms offer high protein content, which is essential for betta fish growth and energy. They are often used as a delicacy to supplement a betta’s diet and encourage natural foraging behaviors.
How often should bettas be fed with bloodworms for optimal health?
It is recommended to feed bettas bloodworms only a few times a week as part of a varied diet. Overfeeding can lead to health issues such as constipation and poor water quality.
What is the recommended amount of bloodworms to give to a betta?
A betta should be fed an amount of bloodworms they can consume in under two minutes. This typically equates to about 3-4 bloodworms per feeding session.
Which is better for betta health: live or frozen bloodworms?
Both live and frozen bloodworms can be healthy options, but frozen bloodworms are less likely to carry parasites and are more convenient to store and handle.
What should be considered when choosing the best brand of bloodworms for betta fish?
When selecting a brand, it’s important to look for high-quality, reputable suppliers that ensure the bloodworms are free from contaminants and disease.
Can a betta fish’s diet consist solely of bloodworms, or is variety important?
A betta’s diet should not consist solely of bloodworms; variety is crucial. A diet that includes pellets, flakes, and other types of live or frozen food is necessary for well-rounded nutrition.

Ian Sterling, founder of Fishlab.com, began his aquarium journey over 30 years ago, driven by a deep fascination for fish and their diverse personalities. His website, Fishlab.com, is dedicated to making fishkeeping accessible and enjoyable, offering beginner-friendly guidance, expert insights, and a community for aquarists to connect and share experiences.