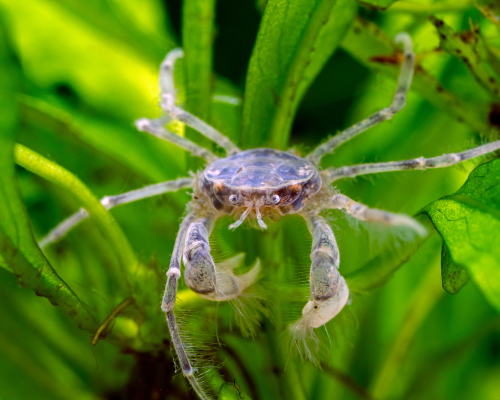
Crabs are fascinating creatures that have a unique place in the marine ecosystem. These crustaceans have a reputation for being scavengers that will eat anything they can find.
However, their diets are more complex than that. In this article, we will explore what crabs eat at home, both in the wild and in captivity.
Understanding crab diets is essential for their survival and wellbeing. Crabs in the wild have access to a variety of food sources, such as algae, plankton, and small fish.
In contrast, crabs in captivity rely on their owners to provide them with a balanced diet that meets their nutritional needs. By examining crab anatomy and feeding mechanisms, we can gain insight into what they need to thrive.
Contents
Key Takeaways on What Do Crabs Eat at Home?
- Crabs have a more complex diet than just scavenging.
- Understanding crab diets is crucial for their survival and wellbeing.
- Examining crab anatomy and feeding mechanisms can provide insight into their nutritional needs.
You will also like these other related posts:
Understanding Crab Diets

Crabs are omnivorous creatures that consume a variety of foods to maintain a balanced diet. They are known to eat both plant and animal matter, including algae, small fish, mollusks, and crustaceans.
Protein is an essential part of a crab’s diet, and they require a significant amount to support their growth and development. They obtain protein from various sources, including small fish, shrimp, and other crustaceans.
Calcium is another vital nutrient that crabs need to maintain their exoskeletons. They obtain calcium from their diet, and it is essential for their overall health and survival.
To ensure that crabs receive proper nutrition, it is essential to provide them with a balanced diet that includes a variety of foods. A balanced diet should consist of both plant and animal matter, including vegetables, fruits, and protein sources such as shrimp or fish.
It is also important to note that overfeeding crabs can lead to health problems such as obesity and digestive issues. Therefore, it is crucial to provide them with the appropriate amount of food based on their size and activity level.
Crabs in the Wild
There are many different species of crabs found in the wild, each with their own unique diet and feeding habits. In general, crabs are omnivores, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter.
The specific food sources for crabs can vary depending on the habitat they live in, such as the ocean, freshwater, or land.
Ocean Crabs

Crabs that live in the ocean have a wide variety of food sources available to them. Some common food sources for ocean crabs include:
- Fish
- Shrimp
- Squid
- Prey
- Other crustaceans
- Mollusks
- Sea urchins
- Algae
- Seaweed
- Dead animals
Some species of ocean crabs, such as the blue crab and king crab, are known for their love of seafood and will actively hunt for small fish and other marine animals.
Other species, such as scavenger crabs, will eat carrion and dead fish that have washed up on the ocean floor.
Freshwater Crabs
Freshwater crabs, as their name suggests, live in freshwater habitats such as rivers, streams, and lakes. Some common food sources for freshwater crabs include:
- Aquatic plants
- Algae
- Small fish
- Shrimp
- Mussels
- Snails
- Worms
Freshwater crabs are often opportunistic feeders and will eat whatever food sources are available to them in their habitat.
Land Crabs
Land crabs are found in a variety of habitats, including forests, deserts, and coastal regions. Some common food sources for land crabs include:
- Plant matter
- Insects
- Small animals
- Dead animals
- Exoskeleton of other animals
One well-known species of land crab is the fiddler crab, which feeds on algae and detritus found in the sand and mud of coastal regions. Dungeness crabs, another species of land crab, are known for their love of clams and other mollusks.
Crabs in Captivity

Feeding Pet Crabs
When it comes to feeding pet crabs, it is important to mimic their natural diet as much as possible. This means providing them with a variety of foods that are rich in vitamins and minerals.
In captivity, it is recommended to feed crabs a combination of both animal and plant-based foods.
Some good options for animal-based foods include insects, krill, snow crab, and chicken. These foods are high in protein and can help support the growth and development of pet crabs.
It is important to note that crabs have small mouths and claws, so it is best to offer them small pieces of food that they can easily consume.
For plant-based foods, pet owners can offer their crabs lettuce, spinach, zucchini, apples, peach, and other vegetation. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that are important for maintaining a healthy crab.
Aquarium Crabs
In addition to providing a balanced diet, it is important to ensure that the aquarium environment is clean and free of any harmful substances. This includes avoiding the use of pesticides or other chemicals that can be harmful to crabs.
Pet owners should also be aware of any parasites or diseases that can affect crabs. It is recommended to purchase crabs from reputable pet stores to minimize the risk of introducing any harmful parasites or diseases into the aquarium.
Crab Anatomy and Feeding Mechanisms
Crabs are fascinating creatures with unique body structures and feeding mechanisms that allow them to thrive in their environments. Understanding their anatomy and feeding habits can help us better care for them in captivity.
Crab Claws

One of the most recognizable features of crabs is their claws, which are used for a variety of purposes.
The larger claw, known as the crusher claw, is used for crushing and breaking open hard-shelled prey, while the smaller claw, called the cutter claw, is used for cutting and tearing. Some species of crabs have claws that are specialized for different tasks, such as digging or climbing.
Crab claws are also used for defense, as they can deliver a powerful pinch to potential predators or competitors. In captivity, it’s important to provide crabs with objects to grip and pinch, such as shells or rocks, to satisfy their natural behaviors.
Crab Mouth and Teeth
Crabs have a unique feeding mechanism that involves grinding their food with their stomachs rather than chewing with their mouths. Their mouths are located on the underside of their bodies and are surrounded by small, sharp teeth that help break down food.
Crabs are omnivorous, meaning they eat both plant and animal matter. Some species of crabs are scavengers, feeding on dead animals and plant material, while others are predators that hunt live prey.
In captivity, it’s important to provide a varied diet that includes both animal and plant-based foods, such as algae, shrimp, and fish.
Crab Sensory Systems and Hunting

Crab Antennae
Crabs use their antennae to sense the environment around them. These appendages are located on the front of the crab’s head and are used for a variety of purposes. The antennae are covered in tiny hairs that are sensitive to touch, vibration, and chemical cues.
One of the most important functions of the antennae is to help the crab locate food. The hairs on the antennae are able to detect the scent of prey, allowing the crab to follow the trail to its source. The antennae also help the crab locate potential mates and avoid predators.
Crab Chemoreceptors
Crabs have chemoreceptors located on their antennae and mouthparts that allow them to detect chemical stimuli in their environment. These receptors are able to detect a wide range of chemicals, including those produced by prey, predators, and potential mates.
Chemoreceptors are essential for crabs to locate food. By detecting the chemicals produced by their prey, crabs are able to follow the scent trail to the source of the food. The receptors also help crabs to avoid toxic substances and locate potential mates.
Crab Nutritional Needs
Crabs are omnivores, which means they eat both plants and animals. They require a balanced diet to stay healthy and thrive in their environment. The following are some of the nutritional needs that crabs require:
1. Protein
Protein is essential for the growth and repair of the crab’s body tissues. Crabs need a high-protein diet to maintain their muscle mass and develop their exoskeleton.
Some of the protein sources that crabs eat include fish, shrimp, clams, and other small crustaceans.
2. Calcium
Calcium is an essential mineral that crabs need to build and maintain their exoskeleton. Crabs absorb calcium through their food, and they also require a source of calcium in their environment.
Some of the calcium-rich foods that crabs eat include shrimp, oysters, and other shellfish.
3. Vitamins

Crabs require a range of vitamins to maintain their health and well-being. Some of the essential vitamins that crabs need include vitamin A, vitamin B12, and vitamin D.
These vitamins help support the crab’s immune system, promote healthy growth and development, and aid in the absorption of other nutrients.
4. Nutrition
Crabs require a balanced diet that includes a variety of different nutrients. They need carbohydrates for energy, fats for insulation and energy storage, and fiber to aid in digestion.
Crabs also require a range of minerals, including potassium, sodium, and magnesium, to maintain their bodily functions.
5. Minerals
Minerals are essential for the proper functioning of the crab’s body. They play a role in everything from muscle contraction to nerve function.
Crabs require a range of minerals, including calcium, magnesium, and potassium, to maintain their health and well-being.
Understanding the Lifespan of Crabs: Key Influences and Care

When exploring the lifespan of crabs, it’s crucial to consider various factors that significantly influence their longevity. Typically, the lifespan of crabs varies depending on the species, with some living only a few years while others can thrive for decades. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Species-Specific Lifespan: Different species of crabs have varying lifespans. For example, certain small hermit crabs may live for up to 10-15 years, while larger species like the Japanese spider crab can live for several decades under optimal conditions.
- Environmental Factors: The habitat and environmental conditions play a pivotal role in determining a crab’s lifespan. This includes the quality of water, temperature, salinity levels, and the presence of hiding spots or shelters in their habitat.
- Dietary Impact: As with most living creatures, diet is a crucial component in influencing the lifespan of crabs. A balanced diet that replicates their natural food sources, as mentioned earlier, contributes to their overall health and longevity.
- Predation and Human Interaction: In the wild, predation significantly affects the lifespan of crabs. In captivity, improper handling or care can lead to stress and health issues, reducing their lifespan.
- Disease Prevention: Regular monitoring for signs of illness and maintaining clean, stable conditions in their habitat can prevent diseases, which is essential for a long and healthy life.
Human Influence on Crab Diets
Crabs and Pesticides
Crabs are known to be resilient creatures that can survive in various environments. However, human activities have greatly impacted their diet.
Pesticides, for example, are widely used in agriculture and can find their way into the waterways where crabs live. These chemicals can be harmful to crabs and can affect their feeding habits.
Studies have shown that pesticides can reduce the amount of food available to crabs. This can lead to starvation and a decrease in their population.
Additionally, some pesticides can accumulate in the bodies of crabs, which can make them unsafe for consumption by humans.
To minimize the impact of pesticides on crab diets, it is important to reduce the use of harmful chemicals and to properly dispose of them.
Farmers and other agricultural workers should be trained on the safe use of pesticides and should follow guidelines to minimize their impact on the environment.
Crabs in Pet Stores

Crabs are also sold in pet stores as pets. However, the diets of these crabs can be greatly impacted by their living conditions. For example, if crabs are not provided with the proper food, they may resort to eating their tank mates or even their own limbs.
Pet stores should provide proper care and nutrition for crabs to ensure their health and well-being. This includes providing a balanced diet and ensuring that the crabs have access to clean water.
It is also important to educate pet owners on the proper care of crabs to minimize the impact of human influence on their diets.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some good food options for pet crabs?
Pet crabs can be fed a variety of foods, including commercial crab food, fresh fruits and vegetables, and protein sources such as cooked chicken or fish.
It is important to ensure that the food is appropriate for the type of crab you have and that it is cut into small pieces to prevent choking.
What should I feed my freshwater crab?
Freshwater crabs can be fed a diet that consists of commercial crab food, algae wafers, and fresh vegetables like spinach and zucchini. They may also enjoy small amounts of protein like cooked shrimp or fish.
Can crabs eat seaweed or other types of vegetation?
Yes, crabs can eat seaweed and other types of vegetation. Some crabs, such as hermit crabs, may even prefer a diet that is primarily plant-based.
However, it is important to ensure that the vegetation is free from any harmful chemicals or pesticides.
What is the natural diet of wild crabs?
The natural diet of wild crabs varies depending on the species and their habitat. Some crabs are scavengers and will eat dead animals and plants, while others are predators and will hunt for small fish and other crustaceans. Many crabs also eat algae and other types of vegetation.
What do store-bought crabs typically eat?
Store-bought crabs, such as those sold for human consumption, are typically fed a diet that consists of commercial crab food and may be supplemented with fresh seafood like shrimp or fish.
Is tap water safe for pet crabs to drink?
Tap water can be safe for pet crabs to drink, but it is important to ensure that the water is free from any harmful chemicals or additives. It is recommended to use a water conditioner to remove any chlorine or other chemicals from the water before giving it to your crab.
What Do Hermit Crabs Typically Eat?
Hermit crabs are omnivores and in the wild, they eat a varied diet including fallen fruit, decaying wood, leaf litter, plants, grasses, and meat. In captivity, they can be fed commercial hermit crab food, fresh fruits and vegetables, and occasional treats like lean meats or fish.
What Do Hermit Crabs Eat in the Ocean?
Ocean-dwelling hermit crabs primarily scavenge for food. Their diet consists of plankton, small fish, dead marine animals, and vegetation debris. They are known for their opportunistic eating habits and will consume almost any edible matter they come across.
What Does Crab Eat at Home in an Aquarium?
At home in an aquarium, crabs can be fed a variety of foods including specially formulated crab pellets, fresh or blanched vegetables, small pieces of fish, and occasional treats like brine shrimp. A balanced diet is crucial for their health.
What is Included in a Crab’s Diet?
Crabs’ diet can be quite diverse. It includes algae, seaweeds, mollusks, small fish, detritus, and even other crustaceans. They are not picky eaters and will often eat whatever is available in their environment.
Do Crabs Eat Seaweed?
Yes, crabs do eat seaweed. Many crab species, especially those found in the ocean, consume various types of seaweed as a part of their natural diet. Seaweed provides essential nutrients and is a common food source for them.

Ian Sterling, founder of Fishlab.com, began his aquarium journey over 30 years ago, driven by a deep fascination for fish and their diverse personalities. His website, Fishlab.com, is dedicated to making fishkeeping accessible and enjoyable, offering beginner-friendly guidance, expert insights, and a community for aquarists to connect and share experiences.