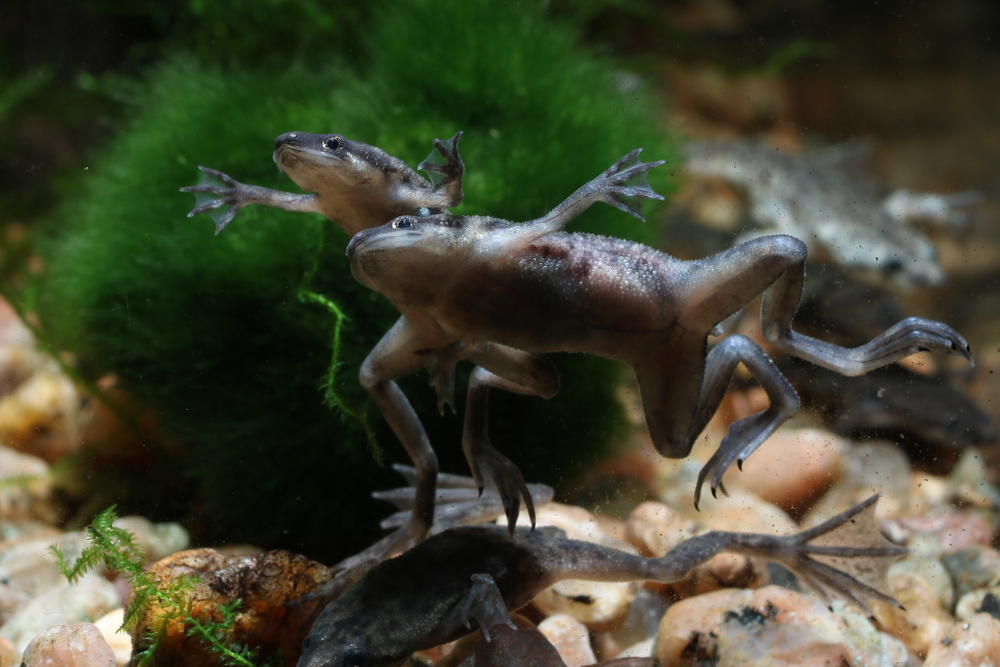
Choosing suitable tankmates is crucial when creating a betta fish habitat. Despite their territorial nature, bettas can live peacefully with certain tankmates in a well-designed aquarium; snails and shrimp are prime examples of such tankmates. But what about African dwarf frogs?
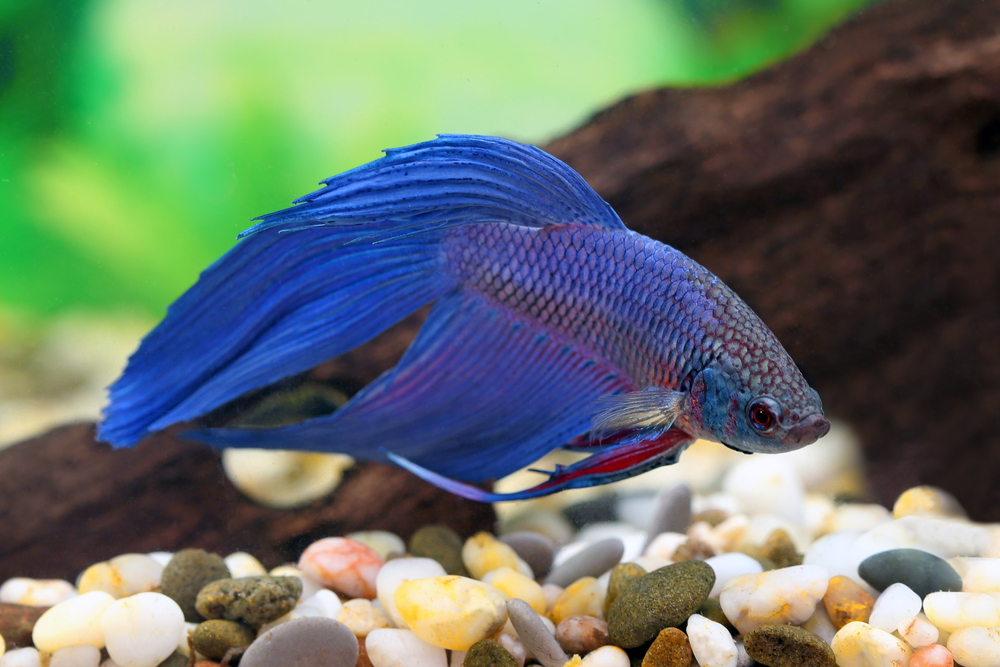

African dwarf frogs are popular aquarium additions. When paired with bettas, understanding their dynamics is important for harmonious cohabitation. Today’s guide is all about understanding the aquatic compatibility between bettas and African dwarf frogs.
To answer whether a betta will kill an African dwarf frog, we will discuss their natural behaviors, habitat needs (tank requirements and water conditions), and feeding habits. Let’s jump right into it, shall we?
Contents
Understanding Betta and African Dwarf Frog Natural Behaviors

Understanding the natural behaviors of betta fish and African dwarf frogs is critical to their harmonious coexistence. These species’ temperaments and activity levels are crucial to their ability to live together.
Check out these other top sought posts:
Betta Fish Natural Behaviors
Betta fish are colorful and popular aquarium pets. Understanding their natural behaviors can help them have a happy and healthy environment. Let’s look at their natural behaviors:
- Solitary Nature: Betta fish are solitary creatures and prefer to live alone. They can become aggressive towards other fish, especially male bettas, so keeping them in separate tanks is best.
- Bubble Nest Building: Male bettas have a unique reproductive behavior-they build bubble nests on the water’s surface using bubbles they create with their mouths. This behavior shows their readiness to breed and can be fascinating in your aquarium. The nests are usually built in quiet. Still, areas of the tank can vary in size and complexity.
- Territorial Behavior: Betta fish are territorial and will defend their space, especially against other male bettas. This behavior can be observed when they flare their fins and display vibrant colors to intimidate perceived threats. Understanding this behavior is crucial when designing the tank layout, as it can help you create separate territories for multiple bettas or provide ample hiding spots for other tankmates.
- Labyrinth Organ: Betta fish have a labyrinth organ that allows them to breathe air from the water’s surface. This adaptation enables them to survive in oxygen-deprived environments.
African Dwarf Frog Natural Behaviors
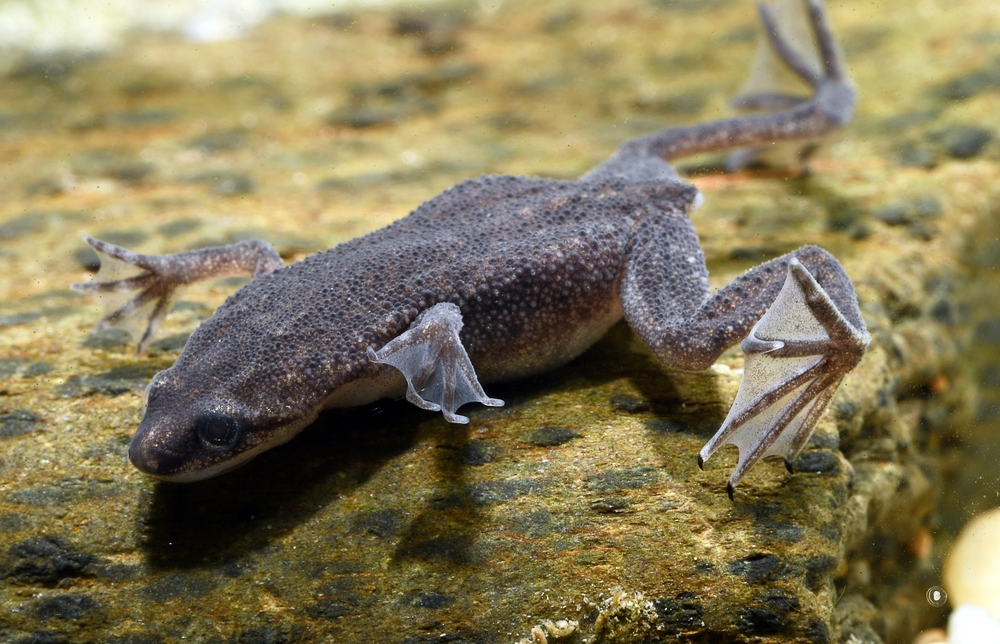

African dwarf frogs are small, aquatic creatures that make charming additions to freshwater aquariums. Understanding their natural behaviors can help you properly care for and introduce tankmates to them. Let’s take a look at their natural behavior:
- Social Creatures: African dwarf frogs are social animals and thrive in groups. To prevent loneliness, you should keep them in pairs or small groups.
- Nocturnal Behavior: These frogs are nocturnal, meaning they are most active at night. Providing hiding spots and dim lighting during the day can help them feel secure.
- Bottom Dwellers: African dwarf frogs spend most of their time at the bottom of the tank, scavenging for food. Provide a soft substrate to prevent injuries to their delicate bodies.
- Vocalizations: These frogs can produce clicking sounds as a form of communication. This behavior is fascinating to observe in your aquarium and provides valuable insights into their social interactions and moods. For instance, a series of rapid clicks may indicate excitement or aggression, while slower, more rhythmic clicks could indicate contentment.
Tank Size and Layout for Coexistence
Regarding tank size, it’s best to set up an aquarium for betta fish and African dwarf frogs, which should be at least 10 gallons. This provides enough space for both creatures to live without invading each other’s territory. For each additional African dwarf frog, add an extra 3 gallons of water to prevent overcrowding.
- Hiding Places: Bettas and African dwarf frogs need space. Make sure their tank has plenty of hiding places, such as caves or PVC tubes. Also, decorations should increase visual appeal and provide vital cover for bettas and African dwarf frogs to feel secure.
- Substrate: Use a soft, fine substrate like sand or smooth gravel to prevent injury to the delicate feet of the African dwarf frogs. This type of substrate is also beneficial for the betta, as they often swim at the bottom of the tank. Avoid using rough or sharp-edged materials that could harm the frogs’ sensitive skin.
- Plants: Plants are vital for aquariums. They oxygenate the water and mimic the natural habitat, providing additional hiding spots for the inhabitants. Use live plants such as Java Ferns and Anubias, which are hardy and do not require intense lighting.
- Lid: Provide a lid to protect bettas and African dwarf frogs from jumping out of the tank.
It’s all about striking a balance between space and the necessary features to foster a diverse yet harmonious ecosystem. By doing so, you demonstrate your commitment to the well-being of your aquatic companions.
Water Conditions and Habitat Parameters

Water conditions hold the utmost importance in the tank environment. Here’s what to consider to be ideal for both species:
- Temperature: These species thrive in a similar temperature range. So keep your heater set to maintain a stable temperature of around 78°F.
- pH Level: A neutral pH level of 7 is perfect. African dwarf frogs and betta fish prefer this, so maintain a regular testing and adjustments routine.
- Lighting: Moderate lighting reflects bettas and African dwarf frog natural environments and provides a regular day/night cycle without promoting excessive algae growth.
- Water Flow and Filtration: Maintaining a suitable water flow and filtration system is vital for the well-being of both betta fish and African dwarf frogs. Make sure the filter is gentle to prevent strong currents that may stress the betta or disrupt the frogs.
By monitoring these parameters and making sure they remain within the right range, you create a stable and healthy habitat that promotes the well-being of both your betta fish and African dwarf frogs.
Feeding and Diet Considerations
Betta fish and African dwarf Frogs are two beloved aquarium residents, and comprehending their feeding habits is crucial to their care. This knowledge equips you with the confidence to keep them healthy and content.
Betta Fish Feeding
Betta fish are carnivorous and enjoy a varied diet. Here are some key points about their feeding habits:
- Bettas are predators and prefer to eat live or frozen foods, such as brine shrimp, bloodworms, and daphnia.
- They should be fed 2-3 times daily, each consisting of only as much food as they can consume in 2-3 minutes.
- Overfeeding can lead to health issues, so it’s important to be mindful of the amount of food you provide.
- In addition to their main diet, you can occasionally offer them small amounts of high-quality flakes or pellets.
African Dwarf Frog Feeding
African dwarf Frogs are omnivorous, meaning they eat plant and animal matter. Their diet should consist of various foods, including small live or frozen invertebrates like bloodworms, brine shrimp, and daphnia. They also enjoy plant matter such as blanched spinach or lettuce. Here’s what you need to know about their feeding:
- These frogs enjoy a diet of small, sinking pellets or tablets and live or frozen foods like bloodworms, brine shrimp, and daphnia.
- Feed them 2-3 times per week, providing only as much food as they can consume in a few minutes.
- Avoid overfeeding, which can lead to water quality issues and health problems.
- You can also offer them small amounts of boiled, chopped vegetables, such as spinach or zucchini, as a supplemental food.
Remember, providing a balanced and appropriate diet will help your aquatic pets thrive and stay healthy in their homes.
Recognizing and Managing Aggressive Tendencies
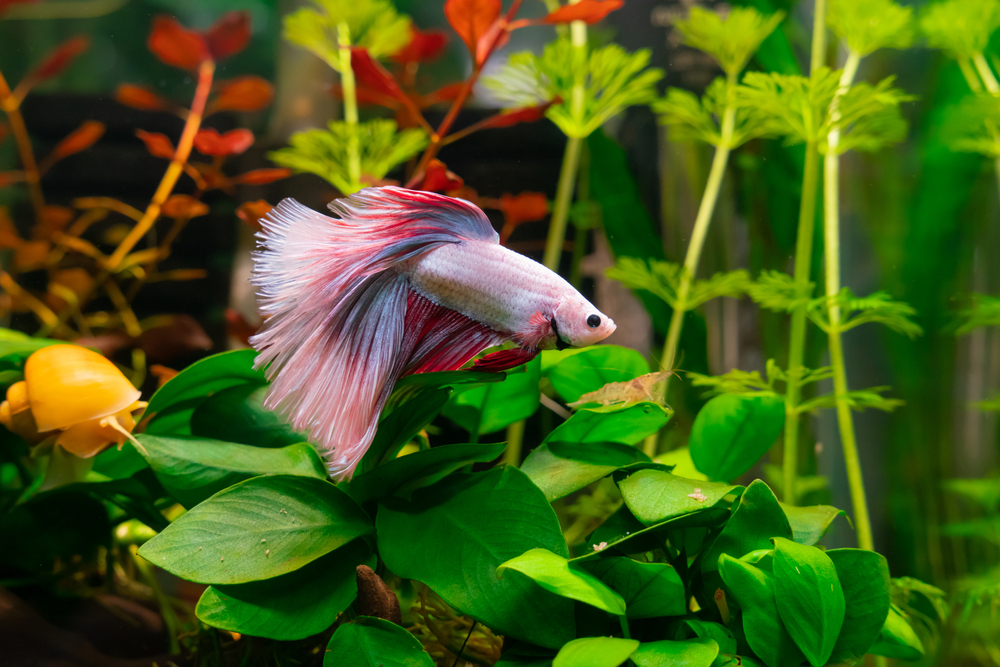

Betta fish and African dwarf frogs can sometimes display aggressive behaviors. Here’s a simple guide to help you recognize and manage their aggressive tendencies.
Betta Fish Aggression
Betta fish can be very territorial and aggressive, especially towards other male bettas. Let’s discuss their signs of aggression and see how you can prevent it.
Signs of aggression in bettas include:
- Flaring their fins and gill covers.
- Chasing and nipping at other fish.
- Some bettas may exhibit tail-biting behavior, nipping at their fins out of stress or aggression.
- Aggressive bettas may exhibit heightened coloration, with brighter and more vivid colors, as a display of dominance and aggression.
To manage betta aggression:
- House your bettas in their tank or with peaceful, non-finnipping tank mates.
- Provide plenty of hiding spots and plants to reduce stress.
- Avoid overcrowding the tank.
African Dwarf Frog Aggression
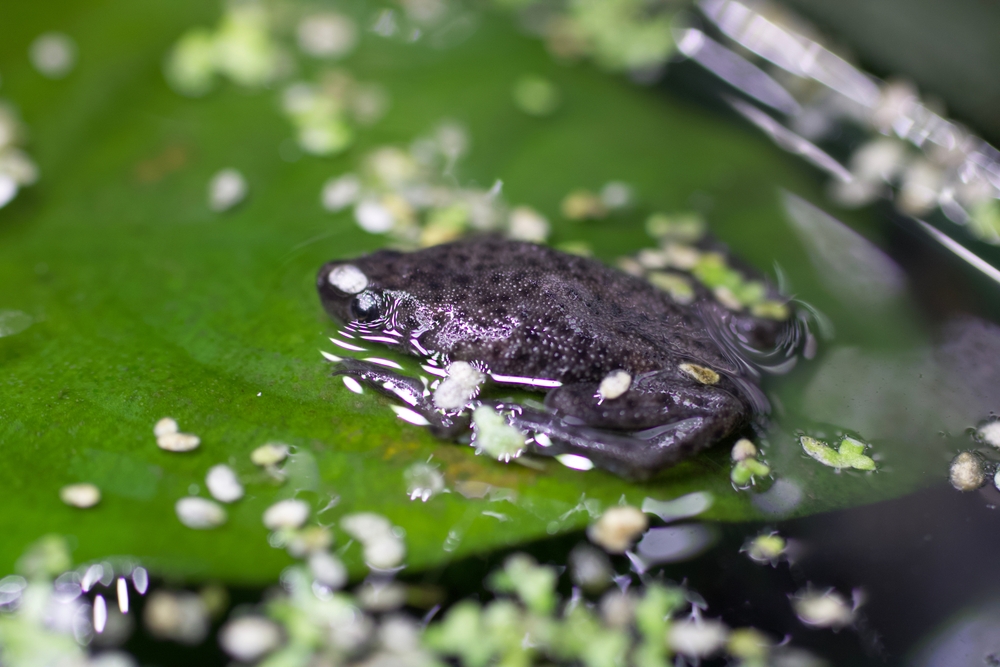

African dwarf frogs are small, cute amphibians who can also be aggressive. They may fight over food or territory in the aquarium.
Signs of aggression in African dwarf frogs include:
- Lunging at each other.
- Biting or grasping other frogs.
- Bumping into and nipping at other tank inhabitants, especially long-finned fish like bettas.
To manage African dwarf frog aggression:
- House them in groups of 3 or more to reduce fighting.
- Provide plenty of hiding spots and plants.
- Feed them a varied diet to minimize competition for food.
Remember, aggression is normal, but excessive fighting can harm your pets. By recognizing the signs and taking steps to manage their environment, you can help keep your betta fish and African dwarf frogs happy and healthy.
Final Thoughts on Will a Betta Kill a African Dwarf Frog?
So that’s it for this guide. While the answer to the question isn’t straightforward, it is evident that these two aquatic creatures can coexist peacefully with the proper setup and a watchful eye.
Remember the key ingredients for a harmonious tank: a spacious home with at least 10 gallons, plenty of hiding spots for both the betta and the frogs, and stable water conditions like cozy temperature and a neutral pH. In addition, remember to feed them properly – betta food for the fish and tasty treats for the frogs.
By following these tips and monitoring their behavior, you can create a beautiful underwater space where your betta can show off its fins and your African dwarf frogs can hop around like little underwater ninjas.
Creating a thriving aquarium for these fascinating creatures can be a fun and rewarding experience. So, if you’ve been thinking about adding lively characters to your underwater paradise, don’t be discouraged by the initial difference between bettas and dwarf frogs.
With some planning and the knowledge you’ve gained from this guide, you can create a peaceful underwater palace for your pets.
Frequently Asked Questions
Betta fish and African dwarf frogs are two popular aquarium pets. Let’s answer some of your most common questions regarding them.
Can I use betta water conditioner for African dwarf frogs?
Yes, you can use betta water conditioner for African dwarf frogs. Betta water conditioner helps remove harmful chemicals like chlorine and chloramine from tap water, making it safe for frogs. Just make sure to follow the dosage instructions on the bottle.
What considerations should be made before adding an African dwarf frog to a betta tank?
You should consider the individual temperaments of your betta fish and ensure that you have a large enough aquarium to prevent overcrowding. Observing your betta’s behavior with tank mates is important, as some may be more territorial.
How do feeding requirements differ between bettas and African dwarf frogs?
Betta fish are primarily carnivorous and prefer foods like brine shrimp or daphnia, while African dwarf frogs eat a more varied diet but can thrive on tubifex worms or bloodworms. Feeding them separately may be necessary to ensure each gets the proper nutrients.
What do African dwarf frogs like in their tank?
African dwarf frogs like a tank with clean, dechlorinated water around 75-78°F (24-26°C). They enjoy hiding places like plants, caves, or decorations. They also like a sandy substrate and gentle water flow.
What other fish can live with dwarf frogs?
African dwarf frogs are peaceful and do well with small, non-aggressive fish like neon tetras, guppies, or corydoras catfish. Avoid keeping them with larger or aggressive fish that might bully or eat them.

Ian Sterling, founder of Fishlab.com, began his aquarium journey over 30 years ago, driven by a deep fascination for fish and their diverse personalities. His website, Fishlab.com, is dedicated to making fishkeeping accessible and enjoyable, offering beginner-friendly guidance, expert insights, and a community for aquarists to connect and share experiences.